The second quarter of 2023 proved to be an exceptionally active period for ransomware groups, posing significant threats to industrial organizations and infrastructure. The rise in ransomware attacks on industrial targets and their consequential impacts highlights the rapid growth of ransomware ecosystems and the adoption of different tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) by these groups to achieve their objectives. In Q2, Dragos observed that out of the 66 groups we monitor, 33 continued to impact industrial organizations. These groups continued to employ previously effective tactics, including exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities, leveraging social engineering, targeting public-facing services, and compromising IT service providers.
In a previous blog post, Dragos assessed with moderate confidence that ransomware groups would intensify their efforts to impact industrial organizations to meet their financial goals, given their dwindling revenues. This assessment proved accurate when analyzing the activities of these ransomware groups in the current quarter. Notably, Dragos witnessed a significant surge in utilizing various initial access techniques. For instance, the Clop group employed new zero-day vulnerabilities in MOVEit Transfer software to target numerous organizations, including major industrial vendors and oil and gas companies. Additionally, BianLian utilized remote monitoring and management (RMM) software, such as AnyDisk. BianLian focused on the data-centric extortion model, while others moved to the double extortion model. Dragos also observed an overlap in victim profiles between some ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) groups, initial access brokers (IABs), and phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) groups.
Dragos assesses with moderate confidence that the third quarter of 2023 will witness increased business-impacting ransomware attacks against industrial organizations for two reasons. Firstly, the prevailing political tension between NATO countries and Russia motivates Russian-aligned ransomware groups to continue targeting and disrupting critical infrastructure in NATO countries. Secondly, as the number of victims willing to pay ransoms diminishes, RaaS groups have shifted their focus towards larger organizations, resorting to widespread ransomware distribution attacks to sustain their revenues. One notable incident in Q2 was the attack on the Port of Nagoya in Japan, which impacted the port’s operations and subsequently affected the supply chains of other industrial organizations, including the Toyota packaging line. Another notable incident was the ransomware attack on the pharmaceutical company Eisai that disrupted their logistics systems, leading to operational disruptions.
Dragos identified 253 ransomware incidents in the second quarter of 2023, an 18% increase from the previous quarter. Dragos analyzes ransomware variants impacting industrial organizations worldwide and tracks ransomware information via public reports and information uploaded to or appearing on dark web resources. By their very nature, these sources report victims that allegedly pay or otherwise “cooperate” with the criminals. However, there is no 1:1 correlation between total incidents and those that elicit victim cooperation. Our breakdown of industrial ransomware activities for this quarter follows.
Your Ransomware Defense
Read our whitepaper to prepare for and respond to a ransomware attack in your OT environment.
Download NowRansomware Incidents by Region
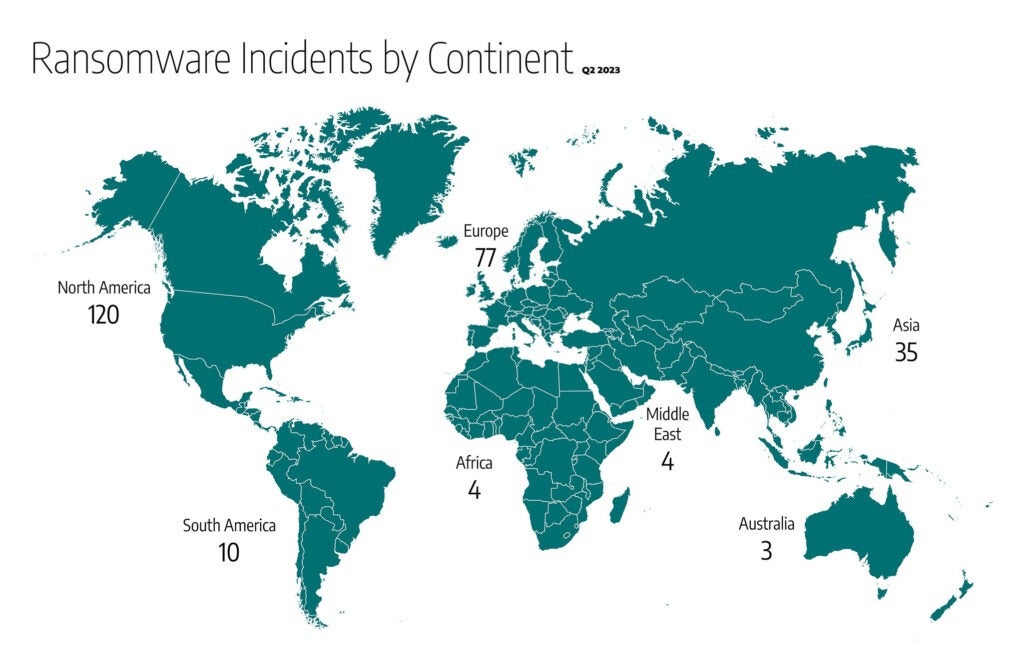
Globally:
- 47.5 percent of the 253 ransomware alleged attacks recorded globally impacted industrial organizations and infrastructure in North America, for a total of 120 incidents, which is an increase of approximately 27 percent over the number we reported last quarter for North America.
- Within North America, the U.S. received over 43 percent of all ransomware incidents, compared to 41 percent last quarter.
- Europe comes in second with 30.5 percent of the global total and 77 incidents, compared to 28 percent or 59 incidents last quarter.
- Asia is next with 14 percent or 35 incidents.
- South America had 4 percent, totaling ten incidents.
- Africa and The Middle East had 3 percent, totaling eight incidents.
- Australia had 1 percent or three incidents.
Ransomware by Sector and Subsector
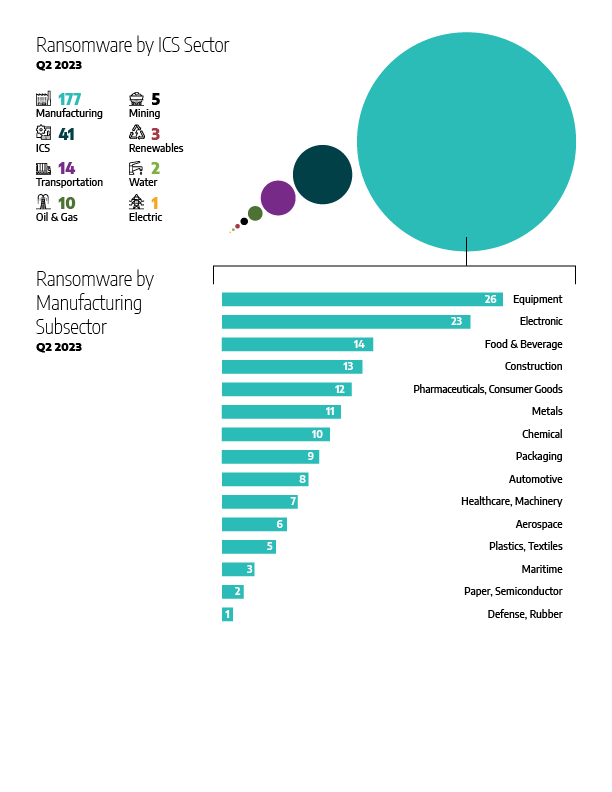
Figure 2 above shows that 70 percent of all alleged ransomware attacks impacted the manufacturing sector (177 incidents total). Next was the industrial control systems (ICS) equipment and engineering sector, with 16 percent of attacks (41 incidents), where 30 incidents impacted ICS equipment entities and 11 incidents impacted ICS engineering entities. The transportation sector was targeted with 5.5 percent (14 incidents). The Oil and Natural Gas sector had around four percent of attacks (10 incidents). The mining sector was impacted by two percent of the attacks (5 incidents). The renewable energy sector had three incidents, the water sector had two incidents, and one incident impacted the electric sector.
The industrial ransomware incidents that Dragos tracked last quarter impacted 20 unique manufacturing subsectors. At the top of the list, equipment manufacturing had around 15 percent (26 attacks), followed by the electronic manufacturing sector with 13 percent or 23 incidents. The remaining manufacturing subsectors that were impacted last quarter break down as follows:
- Food and Beverage – 14 incidents
- Construction – 13 incidents
- Consumer product and pharmaceuticals – 12 incidents each
- Metal – 11 incidents
- Chemicals – 10 incidents
- Packaging – 9 incidents
- Automotive – 8 incidents
- Healthcare – 7 incidents
- Aerospace – 6 incidents
- Plastics and textile – 5 incidents each
- Maritime – 3 incidents
- Semiconductor and paper – 2 incidents each
- Defense and rubber – 1 incident each
Ransomware by Groups

In Q2 of 2023, Dragos tracked the activity of 33 ransomware groups, compared to 20 in Q1 of 2023. Analysis of ransomware data shows Lockbit 3.0 was responsible for 19 percent of the total alleded ransomware attacks, accounting for 48 incidents, nearly a 38 percent decrease compared to the incidents in the last quarter; AlphaV was responsible for 12 percent of attacks (31 incidents); Black Basta was responsible for 10 percent of attacks (26 incidents); 8base and Bianlian next with 15 percent (or 19 incidents each).
The breakdown for the rest of the groups is as follows:
- Play – 16 incidents
- Royal – 14 incidents
- Clop – 13 incidents
- Akira – 9 incidents
- Snatch – 6 incidents
- Blackbyte and Rhyisida – 12 incidents
- Medusalocker and Unsafe – 4 incidents
- Blacksuit, Dunghillleak, Mallox, and Moneymessage – 3 incidents each
- Noescape, Nokoyawa, Qilin, Ragroup, Ransomhouse, and Vicesociety – 2 incidents each
- The remaining ransomware groups were responsible for one percent or less of incidents
The groups we observed in Q1 but not in Q2 2023 are Dark Power, Everest, Lorenz, and Daixin Team. We observed the following ransomware groups for the first time in Q2 2023: 8base, Akira, Rhysida, Blacksuit, Dunghillleak, Moneymessage, Noescape, Nokoyawa, Ragroup, Rancoz, Darkrace, Lapiovra, Malas, Monti, and Trigona. It is still being determined if these new groups are new or reformed from other groups.
What’s Next?
Dragos assesses with high confidence that ransomware will continue to disrupt industrial operations, whether through the integration of operational technology (OT) kill processes into ransomware strains, flattened networks allowing ransomware to spread into OT environments, or precautionary shutdowns of production by operators to prevent ransomware from spreading to industrial control systems. Due to the changes in ransomware groups, Dragos assesses with moderate confidence that new ones will continue to appear as either new or reformed ones in the next quarter. As ransomware groups’ revenues continue to decrease due to victims’ refusal to pay ransoms and government efforts to prohibit this, Dragos assesses with moderate confidence that ransomware groups will increase their efforts to cause damage to industrial organizations in an attempt to fulfill their financial objectives.
Your Ransomware Defense
Ready to put your insights into action?
Take the next steps and contact our team today.
