During the fourth quarter of 2022, ransomware continued to pose substantial financial and operational risk to industrial organizations worldwide. Dragos actively monitors and analyzes the activities of 57 different ransomware groups that have impacted industrial organizations and infrastructure. Dragos observed through publicly disclosed incidents, network telemetry, and dark web postings that out of these 57 groups, only 24 were active during Q4 of 2022. During this time, Dragos became aware of 189 ransomware incidents, a 30 percent increase from the 128 incidents in the previous quarter.
Ransomware groups continue to increase their tools’ efficiencies, enhancing their detection evasion capabilities, and adopting new Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTP). Many ransomware groups rewrote their malware in Rust programming language, including RansomExx, ALPHV, Hive, Luna, and Qilin. Because Rust is a relatively new programming language, anti-virus solutions are unable to understand and analyze it as well as older programming languages, which can provide adversaries with a longer time to impact victim systems before they are detected.1
A growing number of ransomware groups like Black Basta, ALPHV, PLAY, Qilin, and Qyick adopted a new tactic called “intermittent encryption,” which relies on encrypting only parts of the targeted files’ content, enabling faster encryption time. This reduction in encryption decreases the chances of being detected by automated detection tools that rely on detecting abnormal file information operation activities.
Dragos has observed multiple victims who were impacted by two or more ransomware groups last quarter, which indicates the groups may have bought the initial access from the same Initial Access Brokers (IABs) and Wholesale Access Markets (WAM). IABs and WAM are known to use this tactic, in particular, in the initial access that they sell to ransomware groups, raising the risk level that industrial organizations face from ransomware. For example, the following ransomware groups claimed the same victims in the third quarter of 2022:
- Alphav and Vice Society
- Cuba and Karakurt
- LockBit3 and Everest
Lockbit 3.0 accounted for 21 percent of the 189 total ransomware incidents that impacted industrial organizations and infrastructure in the last quarter, down from an annual high of 31 percent last quarter when they introduced its Lockbit 3.0 builder and other new capabilities.
Dragos analyzes ransomware variants impacting industrial organizations worldwide and tracks ransomware information via public reports and information uploaded to or appearing on dark web resources. By their very nature, these sources report victims that allegedly pay or otherwise “cooperate” with the criminals. There is, however, no 1:1 correlation between total targeted attacks and those attacks that elicit victim cooperation. Our breakdown of ransomware activities for this quarter are as follows:
Ransomware by Region
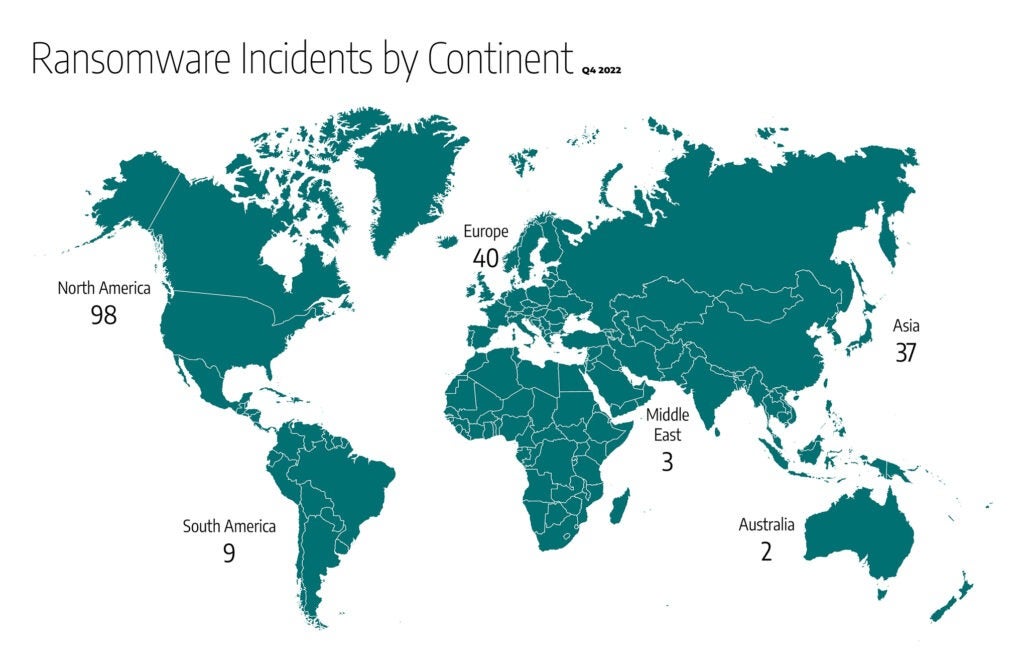
Globally:
- 52 percent of the 189 ransomware attacks impacted industrial organizations and infrastructure in North America, for a total of 98 incidents, more than doubling the number of attacks in the region last quarter, as shown above.
- Within North America, the U.S. received 44 percent of all ransomware attacks, followed by Canada with 8 percent of ransomware attacks.
- Europe comes in second with 21 percent and 40 incidents.
- Asia is next with 20 percent or 37 incidents.
- South America had 5 percent, totaling 9 incidents.
- The Middle East had 2 percent or three incidents.
- Australia had 1 percent or 2 incidents and Africa had no incidents.
Ransomware by Sector and Subsector
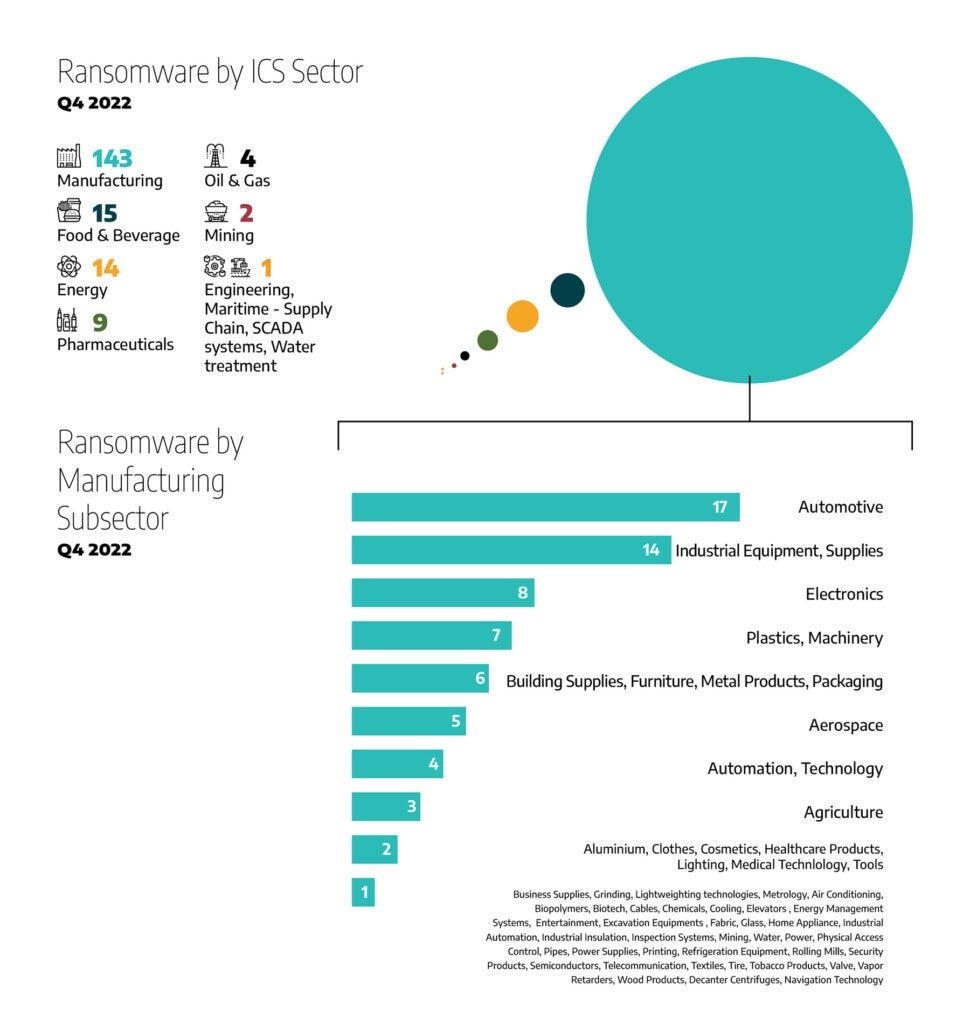
Figure 2 above shows that 76 percent of ransomware attacks impacted the manufacturing sector (143 incidents in total), a 38 percent increase over last quarter. Next, was food and beverage with 8 percent of attacks (15 incidents), which is roughly on par with last quarter. Energy was targeted with 7 percent of the attacks (14 incidents), and pharmaceuticals sectors had 5 percent of attacks (9 incidents). Oil and gas showed two percent (four incidents). The other manufacturing sectors were targeted with one percent or one or less of total attacks in the fourth quarter of 2022. There were no attacks this last quarter on transportation or construction.
The ransomware incidents that Dragos tracked last quarter impacted 147 unique manufacturing subsectors. At the top of the list automotive manufacturing had 12 percent (17 attacks), followed closely by industrial equipment and supplies with 10 percent or 14 attacks. The remaining manufacturing subsectors that were impacted last quarter break down as follows:
- Electronics – six percent.
- Machinery and plastics – five percent each
- Building supplies, furniture, metal products, and packaging – four percent, each
- Aerospace – 3.5 percent of attacks
- Automation, and Technology – three percent each
- Agriculture – two percent of attacks
The remaining subsectors accounted for one percent of ransomware attacks, each.
Ransomware by Groups
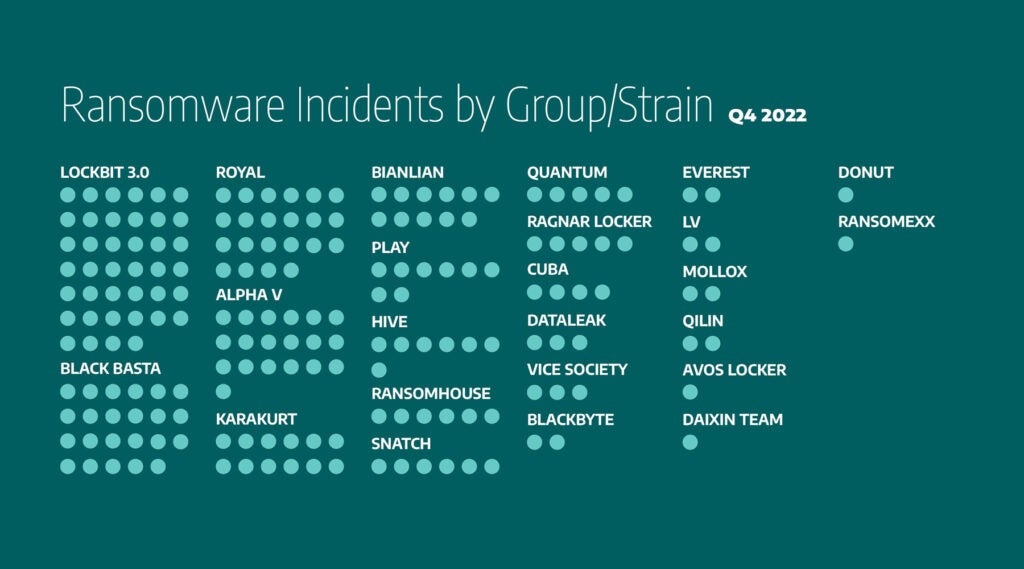
In Q4, Dragos tracked the activity of 24 ransomware groups, one less than Q3 of 2022. Analysis of ransomware data shows Lockbit 3.0 was responsible for 21 percent of the total ransomware attacks, accounting for 40 incidents; Black Basta and Royal came in next with 12 percent, each with 23 and 22 incidents respectively; AlphaV was responsible for ten percent of attacks. BIANLIAN, which first appeared last quarter, accounted for six percent of attacks. The break down for the rest of the groups is as follows:
- KARAKURT: 6 percent (12 incidents)
- Hive and PLAY: 4 percent of attacks, each
- RANSOMHOUSE, Quantum, Ragnar Locker, and snatch: three percent of attacks, each
- Cuba accounted two percent of attacks
- DATALEAK and Vice Society: two percent each
The rest of the ransomware groups were responsible for one percent or less of the attacks.
Ransomware Victimology Trends
During the fourth quarter of 2022, Dragos continued to observe trends in the victimology of ransomware groups. This does not, however, determine the permanent focus of these groups, as victimology can change over time. Dragos observed seven more ransomware groups impacting industrial sectors and regions of the world in this last quarter than in Q3 of 2022. Based on our analysis of the Q4 2022 timeframe, Dragos observed some of the most active ransomware groups impacting the following industries:
- AlphaV: energy, food and beverage, oil and gas, manufacturing
- BIANLIAN: energy, engineering, food and beverage, mining, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing
- Black Basta: food and beverage, manufacturing
- Karakurt: energy, food and beverage, oil and gas, pharmaceutical and manufacturing
- Lockbit 3.0: food and beverage and manufacturing
- Royal: energy, food and beverage, oil and gas, pharmaceutical, and manufacturing
- Avos Locker only impacted Paraguay
- DAIXIN TEAM only impacted Indonesia
- DONUT only impacted the U.S.
Groups that we observed in Q3 but not in Q4 are: Cl0p Leak, Yanluowang, Onxy, Everest, Revel, Stormous, Medusalocker, and Lorenzo. The following groups were observed in Q4 but not in Q3: Qilin, Mallox, Royal, Project Relic, Play, and The DataLeak.
What’s Next?
Dragos assesses with high confidence that ransomware will continue to disrupt industrial operations, whether through the integration of operational technology (OT) kill processes into ransomware strains, flattened networks allowing ransomware to spread into OT environments, or precautionary shutdowns of OT environments by operators to prevent ransomware from spreading to OT systems.
Due to the changes in ransomware groups and the leaking of the Lockbit 3.0 builder, Dragos assesses with moderate confidence that new ransomware groups will appear as either new or reformed ones in the next quarter.
As some governments are considering an outright ban on ransomware payment, Dragos assesses with moderate confidence that the ransomware groups’ activities will decrease in the countries where the payment is banned and increase in other countries where they can achieve their financial objectives.
Source:
Ready to put your insights into action?
Take the next steps and contact our team today.
